How the motherboard works-Know here at UAE Technician Dubai
How the motherboard works- what it is composed of, what different models there are and what it is used inside the computer.
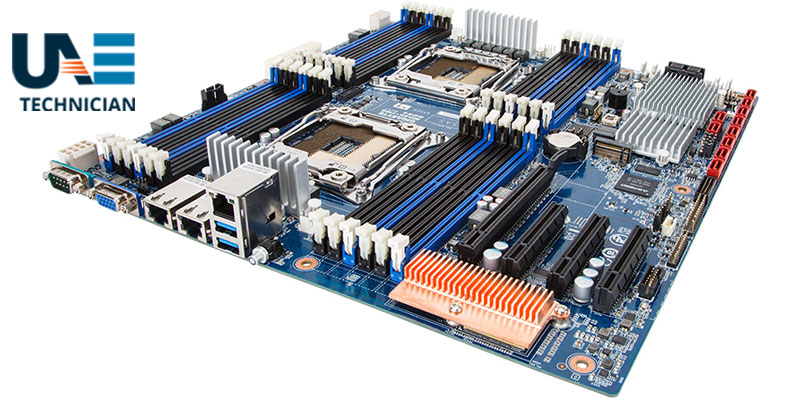
When you open the case of a computer to see what’s inside, the first thing you notice is a large large shelf with several connectors on top and many transistors, namely the motherboard.
What is a motherboard?
The motherboard is the printed circuit where various components work in unison to make the computer work, in which the different parts within it work together to transmit data to each other.
A motherboard allows all parts of the computer to receive energy and communicate with each other.
You can think of the motherboard as the headquarters of a large company, the headquarters where decisions are made, where tasks are assigned to employees.
A motherboard, by itself, is a useless piece that has no internal functions, but is also a necessary piece without which a computer would not exist.
The main task of the motherboard is to hold the computer’s microprocessor chip and let everything else connect to it.
Anything that improves computer performance is part of the motherboard or connects to it through a slot or port.
The problem with motherboards is that there are various types, with different shapes and connections .
Who wants to buy a PC putting together the various pieces must always start from the motherboard, so that the other parts are compatible with it.
1) Form factor: Motherboard attacks Before seeing how a motherboard works it is therefore important to see what form it can have and what differences there are between different models.
The form and layout of a motherboard are called form factor.
The form factor affects the position of the individual components and the shape of the computer case.
While all motherboards work the same way, different card models have different types of ports, sizes and mounting holes.
The most common form factors are:
ATX : the most common, large form (most of which is 12×9.6 inches)
microATX: the smaller version of the standard ATX, which has become very popular in recent years.
Mini-ATX : smaller than the micro version, designed for laptops.
Mini-ITX : smaller than an ATX card (6.7×6.7 inches).
Nano-ITX : for
Pico-ITX thin devices : very small with dimensions of 3.9 x 2.8 inches.
2) CPU Socket: The form factor is just one of many standards that apply to motherboards.
Another important feature that you must always look to be sure of the model you are going to buy is certainly the socket for the microprocessor, which determines the type of Central Processing Unit (CPU) used by the motherboard.
The socket is the housing or the attack of the processor, which is different depending on the brand (Intel and AMD use different Sockets) and also depending on the generation, (older AMD and Intel processors have different sockets from the current ones).
The CPU is that piece of the computer that has the form of a small square with a lot of pins and connectors, which works to interpret and transmit the data made by the northbridge part of a chipset.
Having a high quality CPU is important for the general speed and efficiency of a computer.
3) Chipset
The chipset makes up the logical system of the motherboard and usually consists of two parts: the Northbridge and the Southbridge .
motherboard chipset These are the two most visible and important pieces of the motherboard, which function as two “bridges” connecting the CPU to other parts of the computer.
The chipset is the “glue” that connects the microprocessor to the rest of the motherboard and then to the rest of the computer.
The Northbridge connects directly to the processor via the front side bus (FSB), a memory controller is located on the Northbridge, which provides the CPU with quick access to memory.
The Northbridge also connects to the AGP or PCI Express bus and to the memory itself.
The Southbridge is slower than the Northbridge, and information from the CPU must pass through the Northbridge before reaching the Southbridge.
Other buses connect the Southbridge to the PCI bus, USB ports and IDE or SATA hard disk connections.
Chipset selection and CPU selection go hand in hand, because manufacturers optimize chipsets to work with specific CPUs.
The chipset is an integrated part of the motherboard, so it cannot be removed or updated.
This means that not only the motherboard socket adapts to the CPU, but that the motherboard chipset must work optimally with the chosen CPU.
With different models based on the socket and chipset, when you buy a motherboard today you need to know already what kind of processor you go to mount above it and also, possibly, what kind of updates to do in the future.
Also part of the Chipset is the BIOS , or Basic Input / Output System chip, which controls the basic functions of the computer and performs a self-test every time it is switched on and the CMOS battery , which keeps the basic settings in memory and keeps updated the system time even when the computer is switched off.
Some systems have dual BIOS, which works as a backup in case the other fails or if there is an error during the upgrade.
As for the other motherboard slot attacks we can remember:
Memory slots / DIMMs : used to hold RAM memory
PCI : connect expansion cards such as video card, network card and sound card.
PCIe : a modern version of PCI, with a different interface that can work with almost any type of expansion card.
USB : used for USB connectors.
SATA : used for optical drives / hard drives / solid state drives
4) Data bus: all the above mentioned components would not work in unison without the necessary data buses connecting everything together.
motherboard circuitsWhen we talk about BUS we simply mean the circuit that connects one part of the motherboard to another.
The more data a bus can handle at the same time, the faster the information is able to travel.
The bus speed, measured in megahertz (MHz), refers to the amount of data that can travel simultaneously on the bus.
The bus speed usually refers to the speed of the front side bus (FSB) , the circuit that connects the CPU to the northbridge.
FSB speeds can range from 66 MHz to over 800 MHz.
Because the CPU reaches the memory controller through the northbridge, the speed of the FSB can greatly affect the performance of the computer.
Some of the other buses that can be found on a motherboard are:
the back side bus connects the CPU with the level 2 cache (L2), also known as secondary or external cache.
The memory bus connects the Northbridge to memory.
The IDE or ATA bus connects the Southbridge to the disk drives.
The AGP bus connects the video card to the memory and to the CPU.
The PCI bus connects the PCI slots to the Southbridge.
5) RAM: Another important function of the motherboard is to provide the housing for the RAM memory.
We have determined that the processor clock controls the speed at which a computer thinks, that the speed of the chipset and the bus controls how quickly it can communicate with other parts of the computer.
The speed of the RAM connection, on the other hand, directly controls how fast the computer is to access instructions and data, with a decisive impact on system performance.
Much of the memory available today is the “Double Data Rate” (DDR) memory, but there are several generations of DDR.
When you go to choose RAM care must be taken, therefore, also which type of RAM is supported by the motherboard, if DDR3 or DDR4, which have different compatibility.
6) how the motherboard work Conclusion: Putting everything together:
In a nutshell, when the computer is turned on , electrical power is sent from the power supply to the motherboard and the first data transfers are initiated via the data buses, which cross the Northbridge and Southbridge part of the chipset.
The Northbridge part links the data of CPU, RAM and PCIe, the RAM starts sending inputs to the CPU, which “interprets” these actions as output.
The data on the PCI’s are then transferred to an expansion card, depending on the type you have.
The Southbridge part connects data to the BIOS, USB, SATA and PCI.
The BIOS signals allow the computer to boot, while the data sent to the SATA socket “wake up” the optical drives, the hard disk and the SSD.
SATA data is used to turn on the screen, activate the network connection and the audio.
In short, the motherboard works from headquarters in a computer to transmit data to each of its parts via data buses and is the hardware component that, together with the CPU, better identifies the computer itself, so that changing motherboard or CPU can mean , in fact, change everything as a computer.
For this reason it is essential to choose a motherboard and CPU of a new computer, thinking about the present and also from a future perspective.